Simple Gazebo Example
To install this project, clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/aerostack2/project_gazebo
To start using this project, please go to the root folder of the project.
Launching
The execution on the project is split into two parts: Aerostack2 components and ground station.
Launching Aerostack2
To launch the Aerostack2 components, execute the following command:
./launch_as2.bash
This will open a Gazebo simulation alongside with a tmux session with an Aerostack2 instance for each drone launched.
Launcher offers a few options to customize the execution. ./launch_as2.bash -h will show option list. Options can be set with the following flags:
-m: launch multiagent system simulation. By default not set.-n: select drones namespace to launch, values are comma separated. By default, it launches all drones from world description file.-s: disable launch Gazebo simulator. By default launch simulation.-g: launch using gnome-terminal. By default not set, uses tmux.
Launching Ground Station
To launch the ground station, execute the following command:
./launch_ground_station.bash
Launcher offers a different pool of options to customize the execution. ./launch_ground_station.bash -h will show option list. Options can be set with the following flags:
-m: launch multiagent system simulation. By default not set.-t: launch keyboard teleoperation. By default not set.-v: launch rviz. By default not set.-r: record rosbag. By default not set.-n: select drones namespace to launch, values are comma separated. By default, it launches all drones from world description file.-g: launch using gnome-terminal. By default not set, uses tmux.
Closing
Close all nodes (aerostack2 and ground_station) with the following command executing outside the tmux session:
./stop.bash
Note
The command tmux kill-server will have a similar effect but closing all tmux sessions, so be careful if you have other tmux sessions running.
If launcher was executed with the flag -g, closing should be done manually exiting all gnome-terminal tabs.
Mission execution
The project offers a few examples of mission execution.
Keyboard Teleoperation control: Using reactive teleoperation control. For both single and multiagent swarms.
Python API missions: Using Aerostack2 python API for mission definition. For single drone, using GPS and multiple drones.
Behavior Tree missions: Using Behavior Tree as the mission planner. For single drone only.
Mission Interpreter: Using Aerostack2 mission interpreter. For single drone only.
Keyboard Teleoperation control
In order to launch the components for a single drone, Aerostack2 launcher does not need any additional flags. Just execute ./launch_as2.bash.
This will open a simulation for a single drone alongside the Aerostack2 components necessary for the mission execution.
Gazebo simulator
Ground station should be launched with -t flag to enable keyboard teleoperation. Take a look at the keyboard teleoperation user guide for more information.
A window containing the teleoperation widget should pop up:
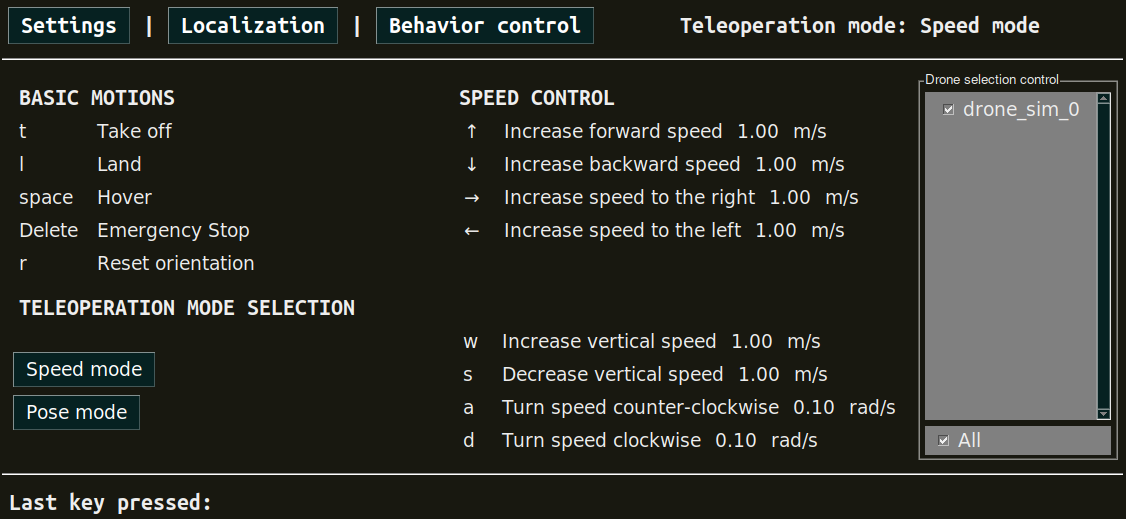
Keyboard teleoperation
Note
The teleoperation widget is also available for multi drone missions. To launch a multi drone simulation, use the flag -m in both launch commands.
Python API missions
In order to launch the components for multiple drones, both launchers require the flag -m.
This will open a simulation for a swarm of drones alongside the Aerostack2 components necessary for the mission execution.
Gazebo simulator
There are three python scripts available for mission execution in the project. For single drone missions, use python3 mission.py for flying a square.
When flying using GPS, use python3 mission_gps.py which will fly a square using GPS waypoints. Here it is what the execution looks like:
For multi drone missions, use python3 mission_swarm.py where a group of drones will fly a swarm coreography. Here it is what the execution looks like:
Note
To understand how missions are built using the Aerostack2 python API, take a look at the Python API reference guide.
Mission Interpreter
Previous missions were defined using python syntaxis. Aerostask2 offers a mission interpreter that allows mission definition using a JSON format.
Currently, the mission interpreter script at the project is only available for single drone missions.
To launch the mission interpreter, execute python3 mission_interpreter.py.
The execution is similar to the python API mission where the drone will fly a square.
Behavior Tree
Missions can also be defined using a behavior tree. The project offers a mission example using a behavior tree for a single drone.
To launch the behavior tree mission, execute python3 mission_behavior_tree.py.
The execution is similar to the python API mission where the drone will fly a square.
Note
Trees can be defined using GUIs like Groot.