Architecture
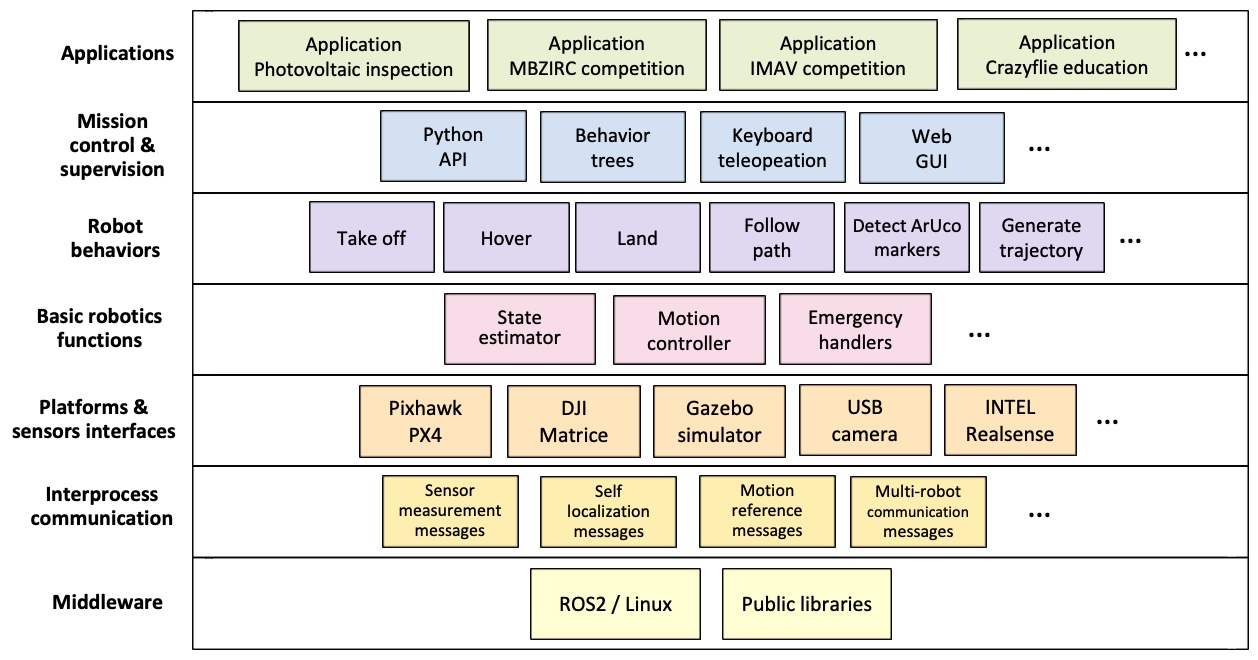
Aerostack2 architecture
Inter-process Communication
It includes components to facilitate communication between processes operating concurrently. These are message types for information exchange that define data structures (specific to aerial robotics) that are common to facilitate process interoperability.
Platform and Sensors
These are components that serve as interfaces with aerial platforms and sensors. Aerostack has several interfaces that allow operating with both physical platforms (e.g., with Pixhawk or with DJI platforms) and simulated platforms (e.g., using simulated drones with the Gazebo environment) besides different kinds of sensors (e.g., USB cameras, RealSense depth camera).
Robotics Functions
Aerostack2 includes a set of software components that implement specialized algorithms corresponding to essential aerial robotics functions for autonomous operation such as state estimation, motion control and other basic functions (e.g., emergency handling, etc.).
Behaviors
Aerostack2 uses a specialized type of component, called behavior, that implements functional robotic abilities such as motion control, motion planning, or perception processing. Behaviors provide a logical layer to formulate mission plans. Using behaviors, a mission plan is expressed as a controlled sequence of activations (or deactivations) of multiple behaviors that may operate concurrently. Each behavior activation initiates the execution of a particular task described with certain parameters (e.g., following a particular path described with a list of waypoints). Compared to directly use of state estimators and actuator controllers, behaviors provide a simple and uniform method to define missions.
Each behavior component corresponds to a specific robot skill allowing self-supervised and streamlined execution of tasks. Depending on the ability addressed by the behavior, it can correspond to motion control, e.g. taking off or hovering, to motion planning, e.g. trajectory generation, or perception processing, e.g. video recording or gimbal control.
Mission Control
This level includes components that facilitate the specification of missions for autonomous drone operation. For example, behavior trees can be used to indicate and visualize with a hierarchical graphical structure the tasks performed by the drone. On the other hand, Aerostack also provides an API (application programming interface) that allows to specify missions in a flexible way using the Python language. This API makes use of another component to abstract relevant information in form of symbolic representation of beliefs. In addition, Aerostack provides tools to the user to monitor and control manually the mission execution.
Applications
The top level corresponds to the specific applications built with the components of the lower levels. Aerostack has examples of applications that can serve developers as a reference and guide on how to build drones that operate autonomously. In addition to applications with real drones, Aerostack has multiple applications on simulated environments with varying degrees of complexity to facilitate learning this technology.